Abstract
In this paper, we consider the following Hardy-type mean field equation
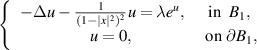 where λ > 0 is small and B1 is the standard unit disc of
where λ > 0 is small and B1 is the standard unit disc of 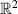 . Applying the moving plane method of hyperbolic space and the accurate expansion of heat kernel on hyperbolic space, we establish the radial symmetry and Brezis–Merle lemma for solutions of Hardy-type mean field equation. Meanwhile, we also derive the quantitative results for solutions of Hardy-type mean field equation, which improves significantly the compactness results for classical mean field equation obtained by Brezis–Merle and Li–Shafrir. Furthermore, applying the local Pohozaev identity from scaling, blow-up analysis and a contradiction argument, we prove that the solutions are unique when λ is sufficiently close to 0.
. Applying the moving plane method of hyperbolic space and the accurate expansion of heat kernel on hyperbolic space, we establish the radial symmetry and Brezis–Merle lemma for solutions of Hardy-type mean field equation. Meanwhile, we also derive the quantitative results for solutions of Hardy-type mean field equation, which improves significantly the compactness results for classical mean field equation obtained by Brezis–Merle and Li–Shafrir. Furthermore, applying the local Pohozaev identity from scaling, blow-up analysis and a contradiction argument, we prove that the solutions are unique when λ is sufficiently close to 0.
Recommended by Dr Kuo-Chang Chen