Semi-structured data is one of the most common types of information that businesses handle today, and yet it’s often misunderstood. Unlike structured data, which fits perfectly into rows and columns, or unstructured data, which has no predefined format, semi-structured data sits in between.
In this guide, we discuss what semi-structured data is, why it’s important, the challenges of working with it, and how you can easily and accurately extract semi-structured data from documents using Docparser, our no-code and AI-powered document parsing solution.
Capture Key Data from Your Documents Easily
Use Docparser to automate data entry, save time, and streamline your document-based workflows.
No credit card required.
What Is Semi-Structured Data?
Semi-structured data is information that doesn’t fit neatly into a traditional database but still carries organizational markers like tags, hierarchies, or key-value pairs. Unlike a spreadsheet, where every field has a strict format, semi-structured data allows flexibility while preserving identifiable structure.
What are some semi-structured data examples?
Semi-structured data is found everywhere in modern workflows:
- Emails can contain structured fields like sender, recipient, and subject, but also unstructured text in the body.
- JSON and XML files are widely used in applications because they store information with tags and attributes, while allowing room for flexible content.
- Log files from servers or applications also fall into this category. They follow a general pattern but can vary depending on the event being captured.
- Product catalogs, too, can be semi-structured, since attributes like size, color, or material may differ from one product to another.
Overall, semi-structured data captures context-rich details without forcing information into rigid formats, which makes it highly valuable in business operations and communications.
What about structured data and unstructured data?
Structured data is the most familiar type of data to businesses. As the name suggests, it’s information stored in neatly organized formats such as databases and spreadsheets.
Every piece of data fits into a defined schema e.g., customer IDs, transaction amounts, or dates stored in columns and rows. Because it is consistent and predictable, structured data is easy to analyze using traditional tools like SQL.
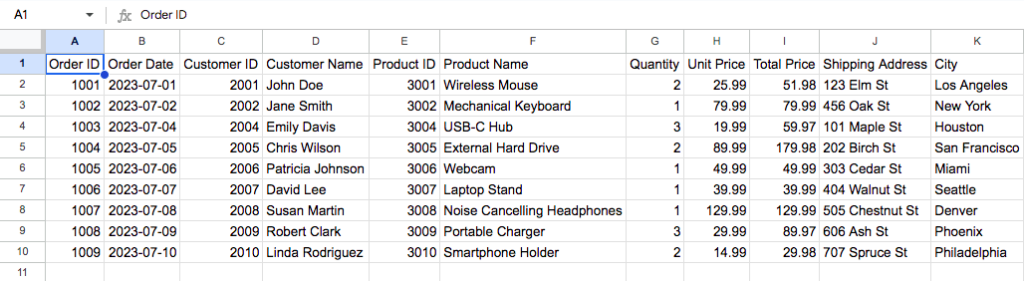
This is an example of structured data extracted from a CSV file using Docparser.
Unstructured data, on the other hand, has no predefined format. This includes documents, images, videos, audio recordings, and free-form text. Common examples of unstructured data include chat logs, recorded phone calls, and messages written by customers.
Unstructured data is more difficult to analyze because there are no rules about how the information is organized. While unstructured data often holds valuable insights, extracting them requires more advanced methods like natural language processing (NLP) or image recognition.

What’s the difference between structured and unstructured data?
The difference lies in organization and usability. Structured data is machine-readable from the start. It’s quick to search, sort, and analyze because every field has a place and a definition. For example, querying a database for all orders placed in the last 30 days is straightforward.
Unstructured data, by contrast, has no set schema. Think of a PDF contract or an audio file: both contain valuable information, but machines can’t easily parse it without specialized tools. Businesses often find unstructured data harder to work with, yet it represents the largest share of information generated today.
What is the difference between structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data?
The key difference is the level of organization. Structured data is fully organized, unstructured data is not organized at all, and semi-structured data sits in the middle.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between these three types of data:
Types of data | Definition | Examples | Key Characteristics |
Structured data | Highly organized and stored in fixed fields | Databases, spreadsheets, CRM records, financial transactions | Easy to search, query, and analyze; rigid schema |
Semi-structured data | Partially organized with tags, labels, or hierarchies | Emails, XML and JSON files, log files, product catalogs | Flexible structure; not as rigid as databases but more organized than free text |
Unstructured data | No predefined format or schema | Images, videos, PDFs, chat transcripts, support ticket emails written in free text | Rich in information but difficult to analyze without advanced tools |
Understanding these differences helps businesses decide which tools to use for storage, analysis, and automation.
Capture Key Data from Your Documents Easily
Use Docparser to automate data entry, save time, and streamline your document-based workflows.
No credit card required.
Why Is Semi-Structured Data Important?
Semi-structured data bridges the gap between rigid databases and free-form content, making it one of the most useful types of information for organizations. It captures details that structured data often overlooks while remaining easier to process than unstructured formats. Because of this balance, businesses rely on semi-structured data for a wide range of applications.
Common use cases include:
- Email management: Extracting key fields like sender, subject, and dates for archiving or analytics.
- E-commerce catalogs: Handling products with varying attributes without creating rigid database schemas.
- Log monitoring: Tracking application and server activity to spot errors or performance issues.
- Customer support systems: Parsing tickets, chat transcripts, and feedback forms for trend analysis.
- Data integration: Exchanging information across platforms using formats like XML or JSON.
In short, semi-structured data provides flexibility, scalability, and richer insights. This makes it highly important for data-driven decision-making.

Extracting Information from Semi-Structured Data Is Often Challenging
While semi-structured data offers flexibility, it also brings unique challenges. Unlike structured data, which is immediately compatible with traditional databases, semi-structured formats don’t always follow a consistent schema. Tags or attributes may vary from one document to another, making it harder to standardize and analyze.
Another challenge is scalability. A small dataset may be manageable, but once you start dealing with thousands of emails, log files, or XML records, the inconsistencies quickly become overwhelming.
Semi-structured data often requires specialized tools to parse, normalize, and transform it into structured formats before you can use it for reporting or analytics. Without the right approach, businesses risk spending more time cleaning data than extracting insights.
How Docparser Helps You Extract Semi-Structured Data from Documents
Inputting semi-structured data manually can be time-consuming and error-prone. The good news is that Docparser automates this process. You can extract the information you need from documents quickly and accurately, and then export it to the business applications you use.
Whether it’s PDFs, invoices, XML files, resumes, contact forms, or other recurring documents, Docparser can handle a wide range of document types and formats.
To extract semi-structured data from documents, you just have to follow this simple, one-and-done setup process:
- Sign up for an account.
- Create a parsing template — you can use pre-set templates, create a blank template, or use our AI-enhanced templates.
- Upload your document(s).
- Create parsing rules manually (very easy to do) or let our AI parsing engine create them for you; either way, you can freely customize your rules.
- Integrate your document parser with a cloud app (or API) to export your data there, or download it as a file.
For a quick overview of how Docparser works, watch this video:
Docparser can handle structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data alike. If you and your colleagues are tired of losing time processing documents manually, Docparser was made just for you. Here’s why users love it:
- Easily extract data from both digital and paper documents. Docparser can identify data in scanned documents and even recognize handwriting, allowing for a wide range of use cases.
- Customize the data extraction process to maximize data accuracy. No more unexpected inaccuracies; you preview the parsing results and refine them during the setup. As a result, error rates drop and you get quality, reliable data to work with.
- Send your parsed data to downstream systems for data analysis. Automatically push extracted data to Excel, Google Sheets, CRM platforms, or other tools for analysis and reporting.
By automating extraction and integration, Docparser helps businesses save time, reduce errors, and unlock insights from data that would otherwise remain trapped in semi-structured formats.
In Conclusion
Semi-structured data strikes a balance between structured and unstructured formats, offering flexibility without losing organization. While it can be challenging to manage manually, tools like Docparser make it easy to extract, standardize, and integrate this data into your workflows.
By automating data capture from PDFs, forms, resumes, and other document types, businesses can save time, reduce errors, and gain actionable insights. Understanding and leveraging semi-structured data is essential for any organization looking to make smarter, data-driven decisions in today’s fast-paced environment. So sign up today and start extracting semi-structured data quickly and accurately.
Capture Key Data from Your Documents Easily
Use Docparser to automate data entry, save time, and streamline your document-based workflows.
No credit card required.