IMDb-BEWERTUNG
7,2/10
9107
IHRE BEWERTUNG
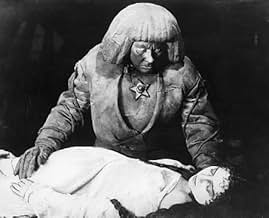
Im Prag des 16. Jahrhundert erschafft ein Rabbi den Golem - eine riesige Figur aus Lehm. Mithilfe der Zauberei erweckt er die Kreatur zum Leben, um die Prager Juden vor der Verfolgung zu sch... Alles lesenIm Prag des 16. Jahrhundert erschafft ein Rabbi den Golem - eine riesige Figur aus Lehm. Mithilfe der Zauberei erweckt er die Kreatur zum Leben, um die Prager Juden vor der Verfolgung zu schützen.Im Prag des 16. Jahrhundert erschafft ein Rabbi den Golem - eine riesige Figur aus Lehm. Mithilfe der Zauberei erweckt er die Kreatur zum Leben, um die Prager Juden vor der Verfolgung zu schützen.
- Regie
- Drehbuch
- Hauptbesetzung
- Auszeichnungen
- 1 Gewinn & 1 Nominierung insgesamt
Hans Stürm
- Der Rabbi Jehuda, der Älteste der Gemeinde
- (as Hans Sturm)
Carl Ebert
- Temple Servant
- (Nicht genannt)
Fritz Feld
- Jester
- (Nicht genannt)
Loni Nest
- Ein kleines Mädchen
- (Nicht genannt)
- …
Ursula Nest
- Little Girl
- (Nicht genannt)
Dore Paetzold
- Des Kaisers Kebse
- (Nicht genannt)
- …
Märte Rassow
- Kind
- (Nicht genannt)
Empfohlene Bewertungen
In 16th-century Prague, a Jewish rabbi (Albert Steinrück) creates a giant creature from clay, called the Golem, and using sorcery, brings the creature to life in order to protect the Jews of Prague from persecution.
Called "one of the most ambitious productions of the silent era" by Mike Mayo, the film is a blend of religion, astrology and black magic -- mixing Judaism with a conjuring of the demon Astaroth.
The film also has an interesting presentation of anti-Semitism, where the emperor accuses the Jews of killing Christ, among other things, and orders them to evacuate the ghetto. How did Germany in 1920 feel about the Jews? We now know how they felt a decade later, but was this hatred always there or invented by Hitler? If it existed, how did it translate to this film's reception by the German people?
Paul Wegener's face is a wealth of visions -- he manages to use his eyes in such a way that present the golem as simultaneously stoic and intensely emotional.
Others have pointed out that Karl Freund's camera is remarkably still for a man who would go on to be known for the most innovative camera techniques in film history (I dare say he is the greatest cinematographer who ever lived). Mayo says there is an "inventive use of extreme camera angles", but I did not notice. The lack of movement does not hinder the film, however.
Lee Price praises the film, saying the only fault of the film is "the inconsistency of the acting", though I did not find it distracting at all (even if the frightened faces of the extras are a bit extreme). Price calls the architecture of the film as influential (or more so) than the German Expressionism of "Caligari". He is not alone in this view: Ivan Butler makes a point to mention the "strange twisted buildings and crooked streets filled with steeple-hatted inhabitants", and Siegfried Kracauer singles out the "maze of crooked streets and stooped houses" devised by Professor Hans Poelzig.
If you are to see or own this film, I recommend the Kino DVD. Not only is the film cleaned up nicely, with a wonderful score and English title cards, but the supplements are beyond what one would expect from such an old film -- featurettes comparing this movie to "Faust" and the later "Le Golem". I enjoyed them.
Called "one of the most ambitious productions of the silent era" by Mike Mayo, the film is a blend of religion, astrology and black magic -- mixing Judaism with a conjuring of the demon Astaroth.
The film also has an interesting presentation of anti-Semitism, where the emperor accuses the Jews of killing Christ, among other things, and orders them to evacuate the ghetto. How did Germany in 1920 feel about the Jews? We now know how they felt a decade later, but was this hatred always there or invented by Hitler? If it existed, how did it translate to this film's reception by the German people?
Paul Wegener's face is a wealth of visions -- he manages to use his eyes in such a way that present the golem as simultaneously stoic and intensely emotional.
Others have pointed out that Karl Freund's camera is remarkably still for a man who would go on to be known for the most innovative camera techniques in film history (I dare say he is the greatest cinematographer who ever lived). Mayo says there is an "inventive use of extreme camera angles", but I did not notice. The lack of movement does not hinder the film, however.
Lee Price praises the film, saying the only fault of the film is "the inconsistency of the acting", though I did not find it distracting at all (even if the frightened faces of the extras are a bit extreme). Price calls the architecture of the film as influential (or more so) than the German Expressionism of "Caligari". He is not alone in this view: Ivan Butler makes a point to mention the "strange twisted buildings and crooked streets filled with steeple-hatted inhabitants", and Siegfried Kracauer singles out the "maze of crooked streets and stooped houses" devised by Professor Hans Poelzig.
If you are to see or own this film, I recommend the Kino DVD. Not only is the film cleaned up nicely, with a wonderful score and English title cards, but the supplements are beyond what one would expect from such an old film -- featurettes comparing this movie to "Faust" and the later "Le Golem". I enjoyed them.
This landmark film is one of the earliest surviving expressionist works, and it's art direction and photography-- while not as stunning as a film like Caligari-- is still extremely interesting with its misshapen sets and its use of light and shadow, and light within shadow. Unlike Caligari, the themes of this film were resonant long after its release, and perhaps still are today.
The Golem is a tolerance film that studies in depth the relationship between Jews and Christians in Prague. To his credit, Wegener refuses to impose stereotypes on either party, instead concentrating on individual characters and using mass characterizations only to highlight the themes of the film.
Unlike stereotypical Jews, rich guys with big noses who rub pennies together, the Jews of Prague are decidedly poor. It is interesting to note that the Jews are all dressed in black and with very few exceptions appear to be bent with age, a tribute to an aging and dying religion. However, they are also portrayed to be earnest and hard-working, with strong communal instincts. The Christians, by contrast, appear bright, shiny, and new. They are dressed in light colors and are young and wealthy, and outwardly appear to be God's new chosen. However, they are also portrayed as foolish bohemians who do not take God seriously. In the end, Christian innocents (and blonde-blue Aryan, coincidentally)are able to stop the Golem's rampage, but only because he allows it. The final shot shows the Star of David lying in the dust as the Jews come to carry their fallen champion back into the ghetto, closing the great door behind them and leaving you with a feeling that they are gone forever. However, it should be noted that the Golem is not only a champion to the Jews, but a symbol of revival.
Another interesting comparison in this film is that between the Golem and Jesus. Like man, the Golem is made of sand and clay, then given life by a supernatural force. They are both immaculate conceptions, with the Golem being motherless while Jesus is born to a virgin mother. Jesus in his time was a champion of the Jews, as is the Golem, and each of them rebelled against the wickedness of the authorities that governed them.
This open-ended presentation of the struggle of Christianity vs. Judaism is what makes this film truly great. I suspect that this relevant elevation above the ordinary is the reason for its survival, even though it is the third film of this series. The fact that Wegener was able to make a film that is so ambiguous is a credit to him considering the circumstances surrounding German film-making at the time.
Rabbi Loew is portrayed as a wise and heroic leader of the Jewish community, which lives in a winding ghetto. He creates the Golem for a noble cause-- to protect his people against eviction by the Christians--and in this cause succeeds after the Christian court is saved by the Golem from divine repudiation after laughing at Loew's presentation of the Old Testament. The creation scene is particularly interesting, not only in its visuals, but for the fact that in this scene Rabbi Loew wears white (for purity), yet performs a ceremony that is holy in nature yet seems like witchcraft. The Golem turns on him when he seeks to continue using the Golem's services for selfish purposes after the Golem has accomplished his mission.
Miriam and Loew's servant are portrayed quite differently. Miriam is a dark seductress who is unwittingly the cause of the Golem's destructive rampage. She is only saved from the hands of the Golem by another act of divine intervention, when the communal prayer of the Jews in the streets of the ghetto results in her release. She usually dresses in dark colors. However, there is also a scene before her affair with Florian in which she wears white (purity of a different kind). Also notice how Florian carelessly twirls a flower when he delivers the edict to Rabbi Loew. This is a brief, but effective, example of his character and foreshadows things to come. Loew's servant is the only other young Jewish character in the film besides a few Jewish children in the street, and it is his revival of the Golem during his jealous rage against Florian that sets the Golem on his destructive path. Like Loew, he is unable to remove the Star of David from the Golem's chest once he begins to use the Golem for selfish gain. In the end, he shares a poignant moment with Miriam where they seek forgiveness and confidence about their actions.
The depth and attention to detail that Wegener shows as a director (and writer) in this film helps to place it among the great films in the brief history of cinema. It's message is particularly haunting considering the events of the next 25 years after its release.
The Golem is a tolerance film that studies in depth the relationship between Jews and Christians in Prague. To his credit, Wegener refuses to impose stereotypes on either party, instead concentrating on individual characters and using mass characterizations only to highlight the themes of the film.
Unlike stereotypical Jews, rich guys with big noses who rub pennies together, the Jews of Prague are decidedly poor. It is interesting to note that the Jews are all dressed in black and with very few exceptions appear to be bent with age, a tribute to an aging and dying religion. However, they are also portrayed to be earnest and hard-working, with strong communal instincts. The Christians, by contrast, appear bright, shiny, and new. They are dressed in light colors and are young and wealthy, and outwardly appear to be God's new chosen. However, they are also portrayed as foolish bohemians who do not take God seriously. In the end, Christian innocents (and blonde-blue Aryan, coincidentally)are able to stop the Golem's rampage, but only because he allows it. The final shot shows the Star of David lying in the dust as the Jews come to carry their fallen champion back into the ghetto, closing the great door behind them and leaving you with a feeling that they are gone forever. However, it should be noted that the Golem is not only a champion to the Jews, but a symbol of revival.
Another interesting comparison in this film is that between the Golem and Jesus. Like man, the Golem is made of sand and clay, then given life by a supernatural force. They are both immaculate conceptions, with the Golem being motherless while Jesus is born to a virgin mother. Jesus in his time was a champion of the Jews, as is the Golem, and each of them rebelled against the wickedness of the authorities that governed them.
This open-ended presentation of the struggle of Christianity vs. Judaism is what makes this film truly great. I suspect that this relevant elevation above the ordinary is the reason for its survival, even though it is the third film of this series. The fact that Wegener was able to make a film that is so ambiguous is a credit to him considering the circumstances surrounding German film-making at the time.
Rabbi Loew is portrayed as a wise and heroic leader of the Jewish community, which lives in a winding ghetto. He creates the Golem for a noble cause-- to protect his people against eviction by the Christians--and in this cause succeeds after the Christian court is saved by the Golem from divine repudiation after laughing at Loew's presentation of the Old Testament. The creation scene is particularly interesting, not only in its visuals, but for the fact that in this scene Rabbi Loew wears white (for purity), yet performs a ceremony that is holy in nature yet seems like witchcraft. The Golem turns on him when he seeks to continue using the Golem's services for selfish purposes after the Golem has accomplished his mission.
Miriam and Loew's servant are portrayed quite differently. Miriam is a dark seductress who is unwittingly the cause of the Golem's destructive rampage. She is only saved from the hands of the Golem by another act of divine intervention, when the communal prayer of the Jews in the streets of the ghetto results in her release. She usually dresses in dark colors. However, there is also a scene before her affair with Florian in which she wears white (purity of a different kind). Also notice how Florian carelessly twirls a flower when he delivers the edict to Rabbi Loew. This is a brief, but effective, example of his character and foreshadows things to come. Loew's servant is the only other young Jewish character in the film besides a few Jewish children in the street, and it is his revival of the Golem during his jealous rage against Florian that sets the Golem on his destructive path. Like Loew, he is unable to remove the Star of David from the Golem's chest once he begins to use the Golem for selfish gain. In the end, he shares a poignant moment with Miriam where they seek forgiveness and confidence about their actions.
The depth and attention to detail that Wegener shows as a director (and writer) in this film helps to place it among the great films in the brief history of cinema. It's message is particularly haunting considering the events of the next 25 years after its release.
At the beginning of the DvD's "scrapbook", there is a quote from Paul Wegener that says he never thought the Golem was an expressionist film. Watching it right after seeing Nosferatu, that statement becomes believable. Despite amazing sets that would have been at home in Caligari, in story, in acting, and in overall tone, The Golem is a much more naturalistic film. Watching it with my son, who is 16, he was struck by its uncomfortable prefiguring of Jewish persecution. I was impressed by the the scarcity of romantic cliches in the story. The golem itself is clearly the ancestor of the Frankenstein monster. Full of wonderful images and interesting as a predecessor of the Universal monster films, The Golem is also very entertaining as a story and as a piece of dramatic film making. Highly recommended.
"Der Golem" is surely one of the best German expressionist silent movies. It may be second only to "The Cabinet of Doctor Caligari"; I enjoyed it as much as Murnau's "Faust", and, truth be told, more than "Nosferatu".
You probably already know the story: it's a well-known Jewish folk tale about a rabbi who constructs a stone creature (a golem) to protect his fellows from an anti-Semitic government in medieval Prague. The creature impresses the gentiles, but then it turns on its master.
These movies aren't really about plot, nor characters. They're about mood, setting, and mise-en-scene. The golem itself is an indelible image; surprisingly it was played by the writer-director himself, who must have been a massive person. You can see the influence on James Whale's classic "Frankenstein". The settings are also sumptuous and fitting.
My mind did wander, but not as much as when I watched Swedish silent "Korkarlen", also a horror film based on local myth. I appreciated that the story was easy to follow and interesting.
You probably already know the story: it's a well-known Jewish folk tale about a rabbi who constructs a stone creature (a golem) to protect his fellows from an anti-Semitic government in medieval Prague. The creature impresses the gentiles, but then it turns on its master.
These movies aren't really about plot, nor characters. They're about mood, setting, and mise-en-scene. The golem itself is an indelible image; surprisingly it was played by the writer-director himself, who must have been a massive person. You can see the influence on James Whale's classic "Frankenstein". The settings are also sumptuous and fitting.
My mind did wander, but not as much as when I watched Swedish silent "Korkarlen", also a horror film based on local myth. I appreciated that the story was easy to follow and interesting.
I caught this restored version of the 1920 German silent classic at Lincoln Center where a new musical score was premiered by the Chamber Music Society. I had never seen the film before and was frankly amazed at the imagery in the sets and costumes and editing of the film. The film's director, Paul Wegener, wearing a thickly padded outfit and wig and high-heeled boots plays the main character, "The Golem". A mythical character from Jewish folklore. For its day, the special effects were also intriguing. I resist describing the movie as anti-semitic but I believe that the portrayal of the jewish ghetto was depicted so dramatically to show that the jews in Prague were outsiders and not welcome in mainstream society. This is evident in the fact that when a nobleman comes to the ghetto, he is greeted by a mammoth closed gate that looks like a precursor to the one used in King-Kong. And most notably, during the creation sequence, a satanic figure appears on screen that would coincide with the European belief a that time that Jews walk hand-in-hand with the Dark forces.
As far as the Golem's performance- this film is really a precursor to "Frankenstein" that Boris Karloff must have seen in its original release - there are so many similarites.
Biggest Image - at the conclusion, the Golem is surrounded by a group of "blond" Aryan-looking children that clearly distinguish them from the ghetto children that we see earlier in the film.
As far as the Golem's performance- this film is really a precursor to "Frankenstein" that Boris Karloff must have seen in its original release - there are so many similarites.
Biggest Image - at the conclusion, the Golem is surrounded by a group of "blond" Aryan-looking children that clearly distinguish them from the ghetto children that we see earlier in the film.
Wusstest du schon
- Wissenswertes"Aemaet", the life-giving word which Rabbi Lowe compels from the spirit Astaroth is also reflected in the bolts of lightning at the end of the creation scene.
- PatzerThe story is set in the 16th Century. A prediction of doom is made based on the movements of Uranus, which was not discovered until 1781.
- Alternative VersionenThe 2002 Alpha Video DVD version runs for 101 minutes. This is not evident from the back of the Alpha Video DVD case, which wrongly lists the running time as only 85 minutes. It looks as if Alpha Video somehow got hold of the fullest version currently known - maybe even a complete version of the film, since there are no obvious gaps in the story.
- VerbindungenEdited into People Who Die Mysteriously in Their Sleep (2004)
Top-Auswahl
Melde dich zum Bewerten an und greife auf die Watchlist für personalisierte Empfehlungen zu.
- How long is The Golem?Powered by Alexa
Details
- Erscheinungsdatum
- Herkunftsland
- Sprache
- Auch bekannt als
- Der Golem - Wie er in die Welt kam
- Drehorte
- Produktionsfirma
- Weitere beteiligte Unternehmen bei IMDbPro anzeigen
- Laufzeit1 Stunde 16 Minuten
- Farbe
- Sound-Mix
- Seitenverhältnis
- 1.33 : 1
Zu dieser Seite beitragen
Bearbeitung vorschlagen oder fehlenden Inhalt hinzufügen

Oberste Lücke
By what name was Der Golem, wie er in die Welt kam (1920) officially released in India in English?
Antwort